Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Computational Physics, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 10088, China
2 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 10088, China
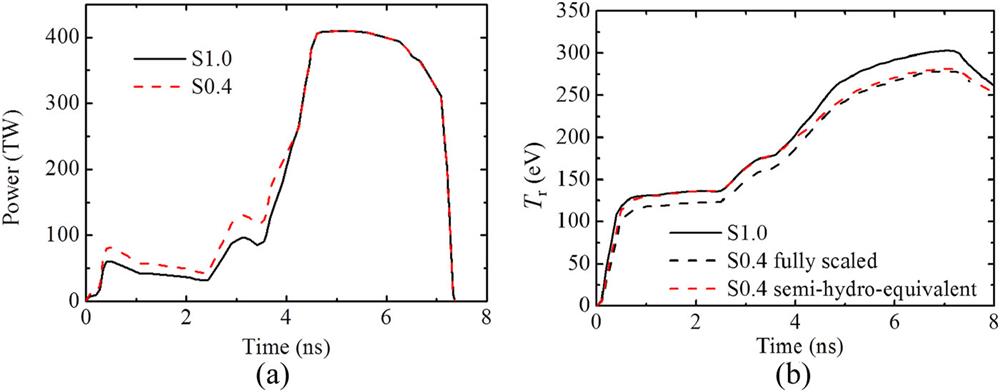
Extrapolation of implosion performance between different laser energy scales is investigated for indirect drive through a semi-hydro-equivalent design. Since radiation transport is non-hydro-equivalent, the peak radiation temperature of the hohlraum and the ablation velocity of the capsule ablator are not scale-invariant when the sizes of the hohlraum and the capsule are scale-varied. A semi-hydro-equivalent design method that keeps the implosion velocity Vi, adiabat αF, and (where PL is the laser power and Rhc is the hohlraum and capsule scale length) scale-invariant, is proposed to create hydrodynamically similar implosions. The semi-hydro-equivalent design and the scaled implosion performance are investigated for the 100 kJ Laser Facility (100 kJ-scale) and the National Ignition Facility (NIF-scale) with about 2 MJ laser energy. It is found that the one-dimensional implosion performance is approximately hydro-equivalent when Vi and αF are kept the same. Owing to the non-hydro-equivalent radiation transport, the yield-over-clean without α-particle heating (YOCnoα) is slightly lower at 100 kJ-scale than at NIF-scale for the same scaled radiation asymmetry or the same initial perturbation of the hydrodynamic instability. The overall scaled two-dimensional implosion performance is slightly lower at 100 kJ-scale. The general Lawson criterion factor scales as (where S is the scale-variation factor) for the semi-hydro-equivalent implosion design with a moderate YOCnoα. Our study indicates that χnoα ≈ 0.379 is the minimum requirement for the 100 kJ-scale implosion to demonstrate the ability to achieve marginal ignition at NIF-scale.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2024, 9(1): 015601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Modern Mechanics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Department of Mathematics and Physics, Nanjing Institute of Technology, Nanjing, JiangSu 211167, China
4 Department of Plasma Physics and Fusion Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, China
5 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 10094, China
The effects of electron nonlocal heat transport (NLHT) on the two-dimensional single-mode ablative Rayleigh–Taylor instability (ARTI) up to the highly nonlinear phase are reported for the first time through numerical simulations with a multigroup diffusion model. It is found that as well as its role in the linear stabilization of ARTI growth, NLHT can also mitigate ARTI bubble nonlinear growth after the first saturation to the classical terminal velocity, compared with what is predicted by the local Spitzer–Härm model. The key factor affecting the reduction in the linear growth rate is the enhancement of the ablation velocity Va by preheating. It is found that NLHT mitigates nonlinear bubble growth through a mechanism involving reduction of vorticity generation. NLHT enhances ablation near the spike tip and slows down the spike, leading to weaker vortex generation as the pump of bubble reacceleration in the nonlinear stage. NLHT more effectively reduces the nonlinear growth of shorter-wavelength ARTI modes seeded by the laser imprinting phase in direct-drive laser fusion.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2022, 7(5): 055902

1 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所,北京 100094
2 北京大学 应用物理与技术研究中心 高能量密度物理数值模拟教育部重点实验室工学院,北京 100871
3 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心,四川 绵阳 621900
4 中国工程物理研究院 上海激光等离子体研究所,上海 201800
5 中国矿业大学(北京),北京 100083
6 中国海洋大学 数学科学学院,山东 青岛 266100
7 安徽大学 物理与材料科学学院,合肥 230039
激光聚变有望一劳永逸地解决人类的能源问题,因而受到国际社会的普遍重视,一直是国际研究的前沿热点。目前实现激光惯性约束聚变所面临的最大科学障碍(属于内禀困难)是对内爆过程中高能量密度流体力学不稳定性引起的非线性流动的有效控制,对其研究涵盖高能量密度物理、等离子体物理、流体力学、计算科学、强冲击物理和高压原子物理等多个学科,同时还要具备大规模多物理多尺度多介质流动的数值模拟能力和高功率大型激光装置等研究条件。作为新兴研究课题,高能量密度非线性流动问题充满了各种新奇的现象亟待探索。此外,流体力学不稳定性及其引起的湍流混合,还是天体物理现象(如星系碰撞与合并、恒星演化、原始恒星的形成以及超新星爆炸)中的重要过程,涉及天体物理的一些核心研究内容。本文首先综述了高能量密度非线性流动研究的现状和进展,梳理了其中的挑战和机遇。然后介绍了传统中心点火激光聚变内爆过程发生的主要流体力学不稳定性,在大量分解和综合物理研究基础上,凝练出了目前制约美国国家点火装置(NIF)内爆性能的主要流体不稳定性问题。接下来,总结了国外激光聚变流体不稳定性实验物理的研究概况。最后,展示了内爆物理团队近些年在激光聚变内爆流体不稳定性基础性问题方面的主要研究进展。该团队一直从事激光聚变内爆非线性流动研究与控制,以及聚变靶物理研究与设计,注重理论探索和实验研究相结合,近年来在内爆重要流体力学不稳定性问题的解析理论、数值模拟和激光装置实验设计与数据分析等方面取得了一系列重要成果,有力地推动了该研究方向在国内的发展。
激光聚变 惯性约束聚变 流体力学不稳定性 高能量密度物理 非线性流动 辐射流体力学 内爆物理 laser fusion inertial confinement fusion hydrodynamic instability high-energy-density physics nonlinear flow radiation hydrodynamics implosion physics 强激光与粒子束
2021, 33(1): 012001
强激光与粒子束
2020, 32(9): 092004
1 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100088
基于新建成的神光Ⅲ主机装置开展了首次激光间接驱动内爆集成实验。国内首次采用多环脉冲整形激光注入黑腔产生X光辐射驱动内爆,通过优化激光打靶参数控制驱动不对称性,演示了以惯性压缩为主、收缩比约15倍的DT靶丸内爆实验能力, 实现了准一维的高静产额(YOC)和高中子产额的物理指标;其中,真空黑腔DT靶丸最高中子产额为1.9×1012,YOC达到60%;充气黑腔DT靶丸最高中子产额为2.4×1012,YOC大约70%。该实验为未来开展多台阶整形辐射驱动、更高倍数收缩比的高压缩内爆综合实验、验证点火靶物理设计和关键调控措施有效性奠定了基础。
激光间接驱动 集成实验 惯性压缩 中子产额 laser indirect-driven integrated experiment inertial compression neutron yield 强激光与粒子束
2016, 28(8): 28080101
1 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100094
总结了在神光Ⅲ原型激光装置上开展的一系列黑腔物理实验研究, 从多个方面研究了黑腔内部等离子体状态和辐射场特性。用真空黑腔能量学研究获得了散射光、辐射温度和不同能段辐射流份额的定标规律, 从能量学角度梳理和分析了整个激光黑腔相互作用过程。通过对黑腔中充入低密度低Z气体抑制了腔壁等离子体运动, 明显减少了可能造成靶丸预热的金M带辐射流(1.6~4.4 keV)份额。针对黑腔内部不同区域等离子体, 研究了光斑区等离子体的运动, 分析了其与电子热传导限流因子的关系; 研究了冕区等离子体的运动, 分析了不同充气等离子体条件对其的影响; 在同一发次实验中同时测量了光斑区与再发射区的辐射流比值。
激光聚变 间接驱动 黑腔物理 能量学 辐射流 laser fusion indirect drive hohlraum physics energetics radiation flux 强激光与粒子束
2015, 27(3): 032014
北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100094
通过理论分析和LARED多群辐射输运模拟研究了激光间接驱动聚变中黑腔辐射温度的角分布特点。研究发现, 黑腔辐射温度角分布主要决定于光斑区与非光斑区的对比度、视野中光斑区的面积比例, 以及体发射的份额。激光二维光环排布下黑腔辐射温度角分布与二维LARED模拟结果非常一致。研究还发现, 二维的LARED模拟能够有效地用于研究神光Ⅲ原型黑腔实验中三维光斑排布下的辐射温度角分布。通过缩小FXRD测量面积能够有效地提高黑腔辐射温度随角度的变化, 从而降低辐射流测量误差对辐射温度角分布的影响。
间接驱动聚变 黑腔 辐射温度 indirect-drive fusion hohlraum radiation temperature LARED LARED 强激光与粒子束
2015, 27(3): 032011
北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100094
介绍了辐射流体力学程序LARED集成程序的物理背景、模型方程、数值方法和数值算例。该程序主要应用于激光间接驱动惯性约束聚变的二维整体模拟, 兼顾激光直接驱动、辐射驱动靶丸内爆过程和流体不稳定性等物理过程的数值模拟。通过与实验数据、一维辐射流体力学程序进行比对, 验证了程序的可靠性。该程序实现了多群输运建模下NIF点火靶的全过程数值模拟, 并已应用于惯性约束聚变的物理研究。
激光惯性约束聚变 LARED集成程序 黑腔 内爆 点火靶 inertial confined fusion LARED-Integration code hohlraum implosion ignition target 强激光与粒子束
2015, 27(3): 032007





